3.4L Buffered bike lanes, unprotected
Search Content
Download PDF
Print Guide
Introduction
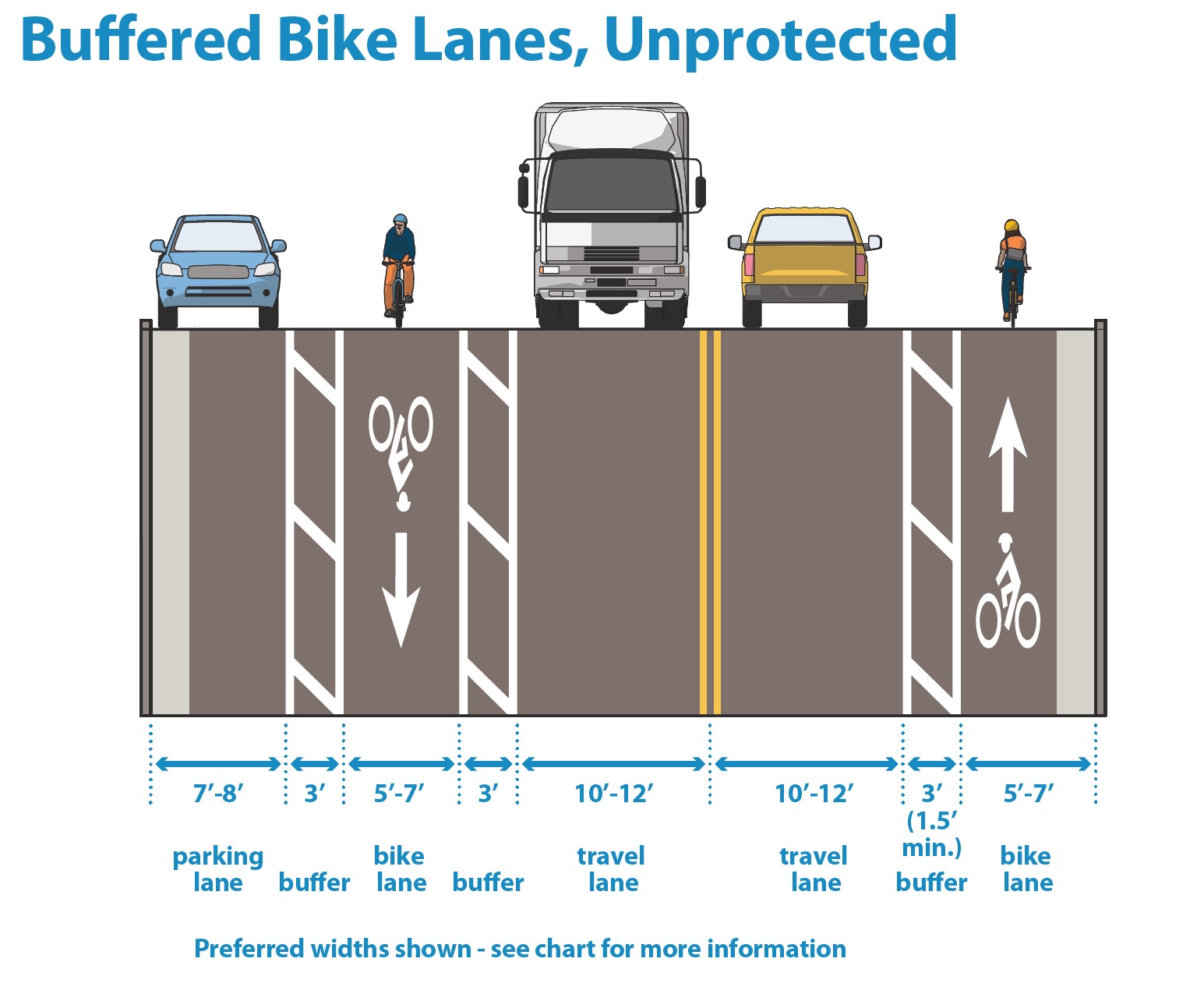
Buffered bike lanes provide additional horizontal separation between the bike and travel or parking lanes, increasing comfort and separation for people biking.
Bike lane buffers should be considered in scenarios where excess roadway space allows for bike facilities wider than 7 feet. Bike lanes or buffered bike lanes may be considered with any street retrofit project that overlaps with the All Ages and Abilities Network. Unprotected bike lanes should generally not be used for street reconstruction projects as they are not low-stress All Ages and Abilities bikeways.
Figure 3.4L.1:
Buffered bike lane dimensions graphic
Design Considerations
|
Dimensions |
|
|
Cross hatching |
Buffers wider than 2’ require cross hatching at 20’ to 60’ spacing. 2-foot or narrower buffers do not require cross hatching. |
|
Width considerations |
Due to the lack of vertical delineation, buffers may be considered part of the overall bike lane width. |
|
Maintenance |
Reliable snow and ice clearance/removal for buffered unprotected bike lanes is challenging, especially when located adjacent to a parking lane. |
|
Intersection guidance |
See also bikeway intersection design guidance. |