3.6 Roadways
3.6H Medians
Search Content
Download PDF
Print Guide
Introduction
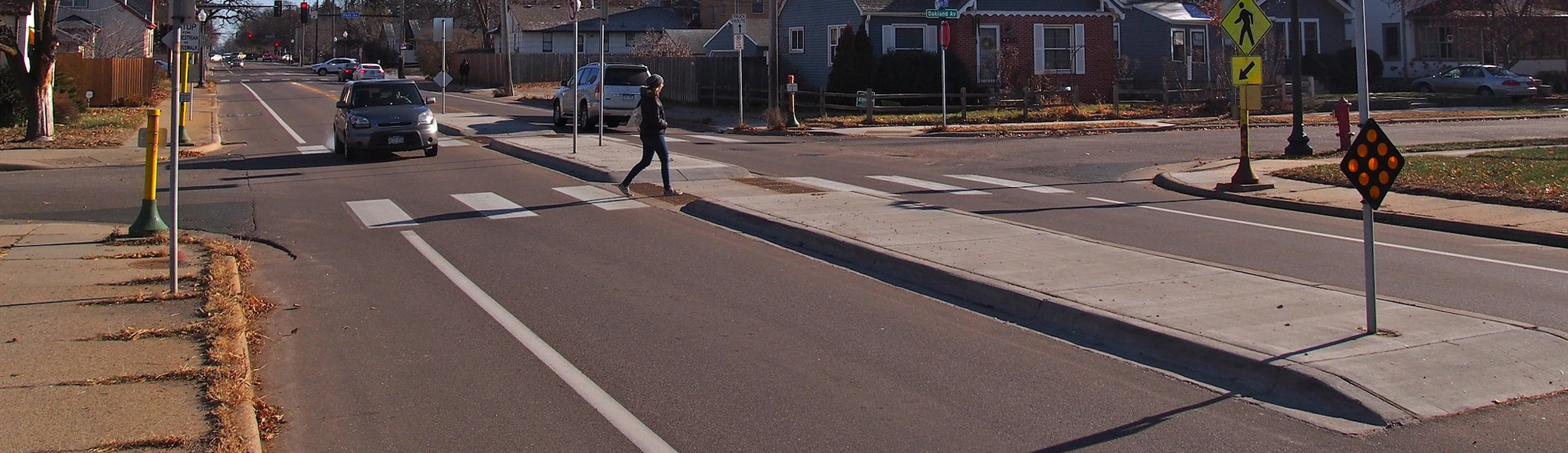
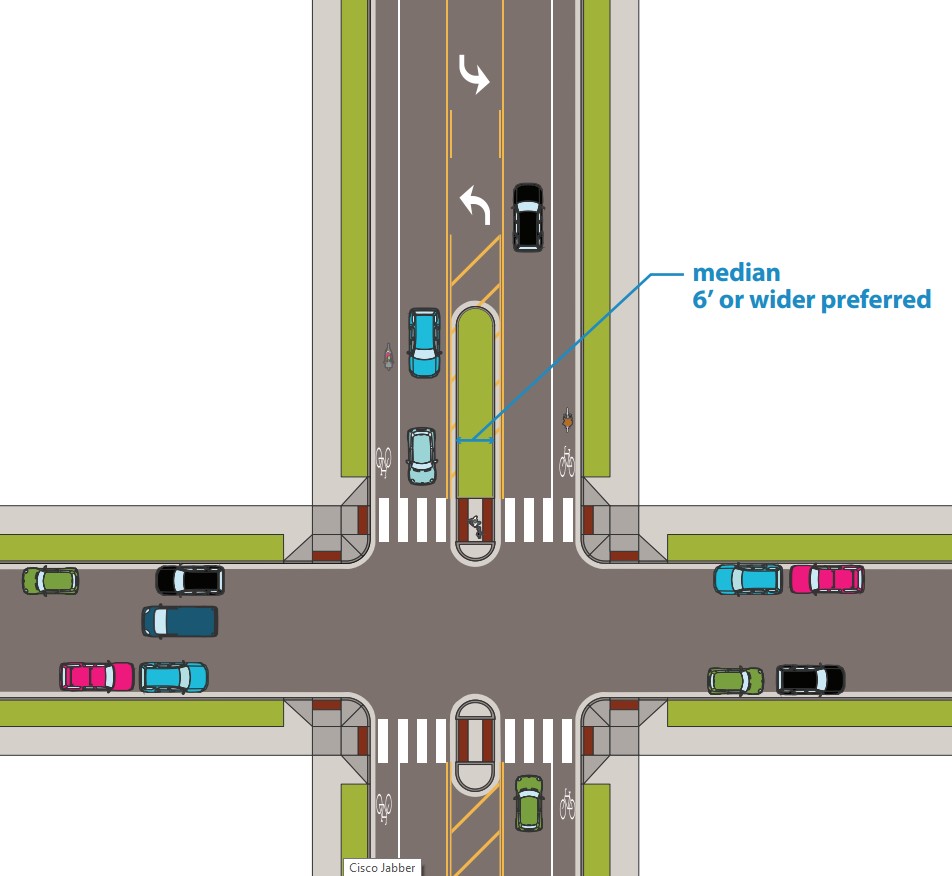
Medians provide a barrier between traffic lanes. They can be used to provide refuge for people walking and biking, to protect against head-on motor vehicle crashes, to prevent turns, and to provide space for greening. Medians can be installed as part of street reconstruction or retrofit projects.
Figure 3.6H.1:
Medians recommended dimensions
Design Considerations
|
Preferred width |
|
|
Greening |
|
|
Curb and gutter |
Standard 6” curb tops and 1’ gutters are generally used adjacent to medians. If there are catch basins adjacent to medians, 2’ gutters should typically be used. |
|
Delineator medians |
Low-cost medians can be implemented using delineators in street retrofit projects. |