3.4C Delineator-protected bike lanes
Search Content
Download PDF
Print Guide
Introduction
Delineator-protected bike lanes utilize plastic delineators or “bollards” and a buffer space between the bikeway and travel or parking lane to provide physical separation from motorized traffic. Delineator-protected bike lanes should only be used with street retrofit projects; use a more robust protected bike lane type with vertical protection with permanent materials for street reconstruction projects.

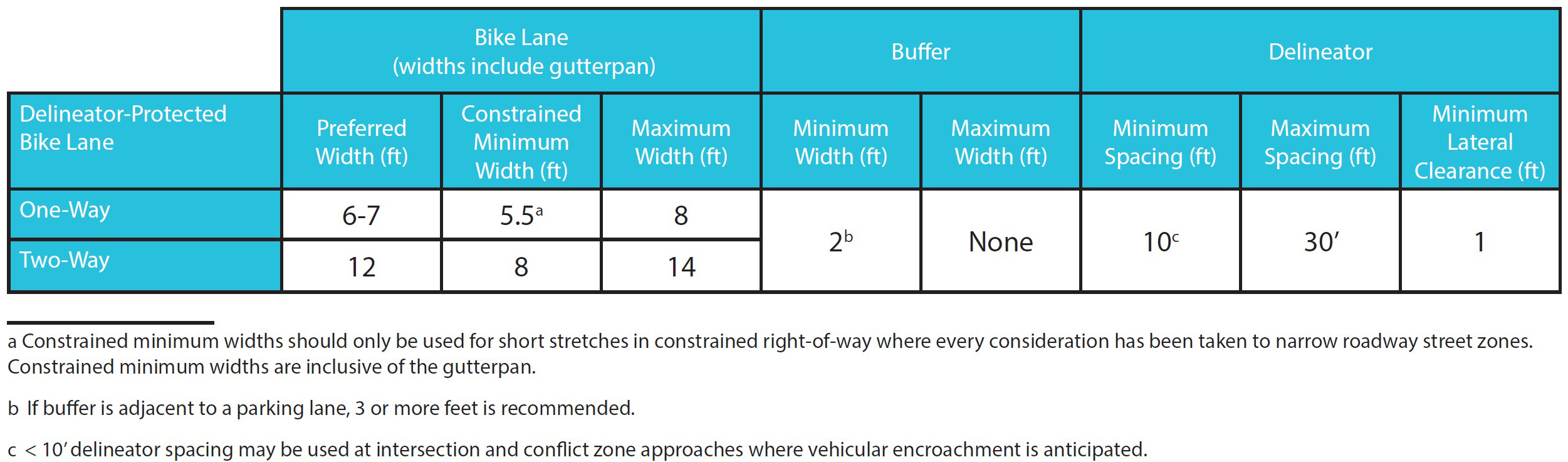
Figure 3.4C.1:
Delineator-protected bike lane dimensions table
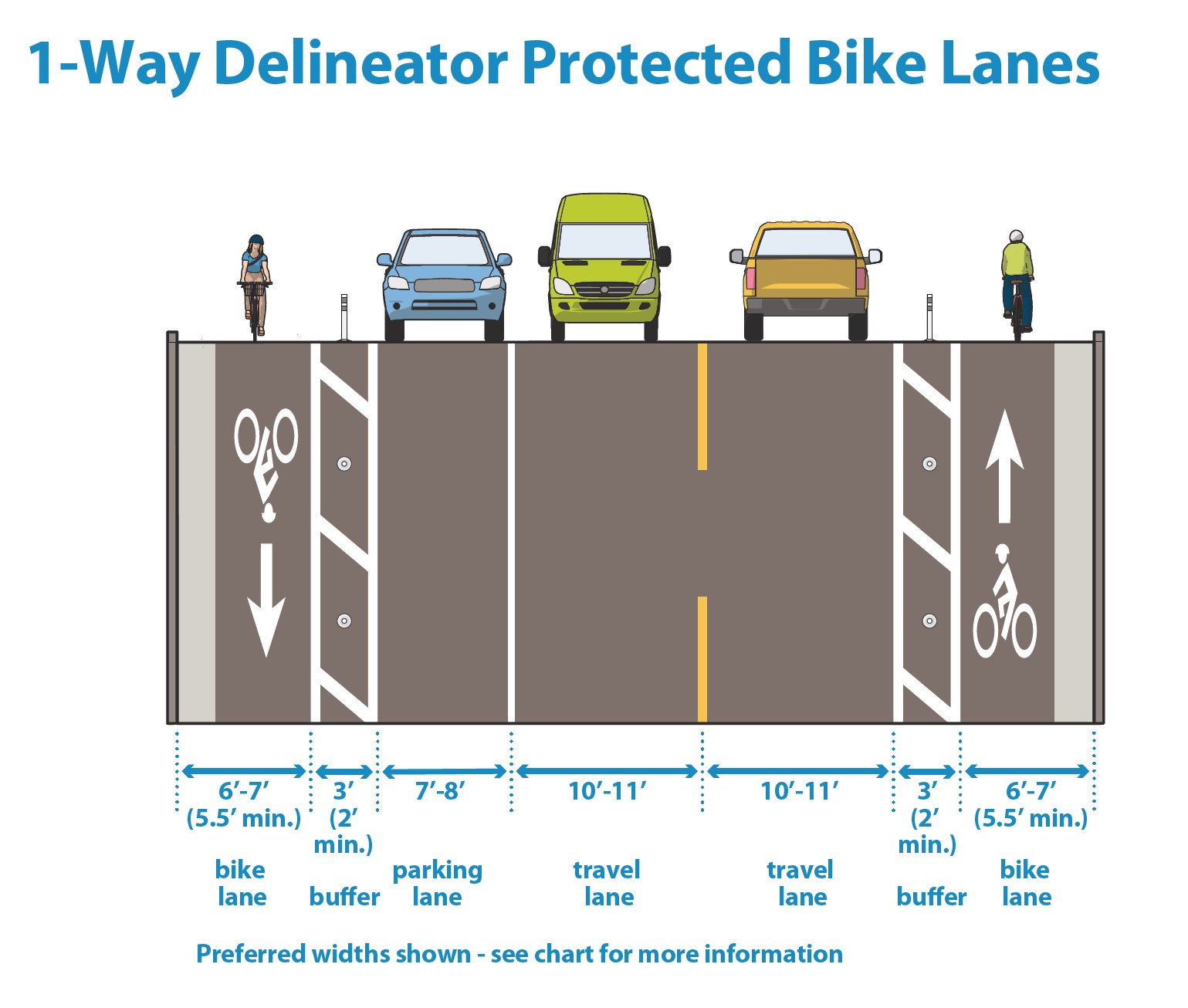
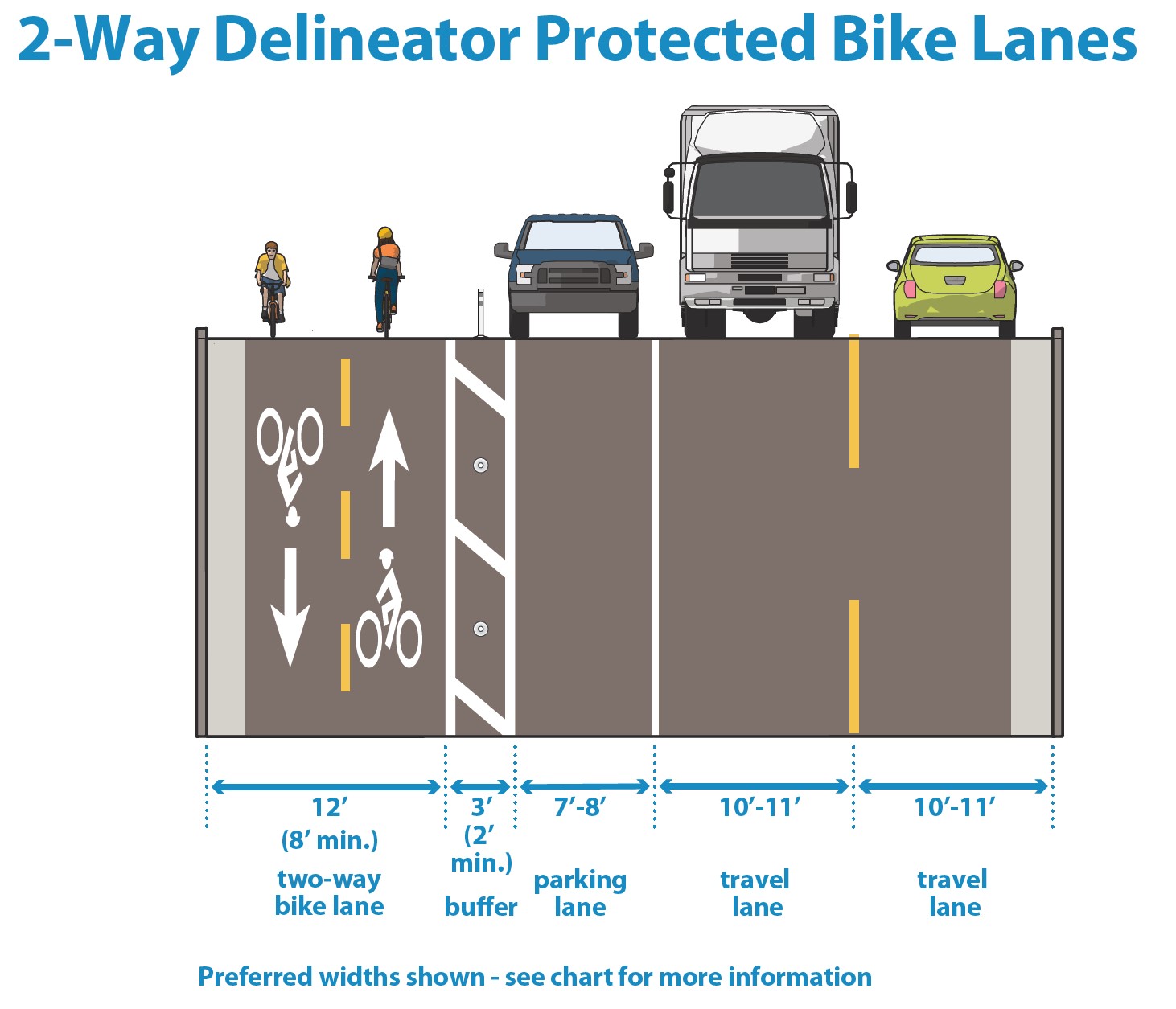
Figure 3.4C.2:
Delineator-protected bike lane dimensions graphic
Design Considerations
|
Operation |
Delineator-protected bike lanes may be designed for one-way or two-way bicycle traffic. |
|
Gutter pan considerations |
Delineator-protected bike lanes directly adjacent to the curb should generally include a minimum of 4 feet of smooth, ridable surface, excluding any adjacent gutter pan. In very constrained right of way where every consideration has been taken to narrow roadway street zones, 3.5’ of smooth, ridable surface can be used for short stretches. |
|
Buffer width |
3’ or wider buffers between the bike lane and traffic lanes are preferred. 2’ buffers can be used for very space-constrained environments provided the location is not adjacent to a parking lane and the bike lane and buffer area generally maintain a minimum combined width of 8’ (including the gutter). |
|
Combined dimensions with parking |
The total minimum combined dimensions of the bike lane, buffer, and parking lane for a one-way parking protected bikeway is:
|
|
Delineator spacing |
Delineators should be centered in the buffer area and spaced at increments between 10’ and 30,’ with closer spacing where vehicular encroachment into the bike lane is anticipated. |
|
Bike lane width |
Wider bike lanes are preferred in environments with higher bicycle volumes to support passing. |
|
Buffer width |
Wider buffers are preferred on corridors with a high percentage of heavy vehicles, established loading zones, and where adjacent parking utilization and/or turnover is high. |
|
Parking lane considerations |
|
|
ADA considerations |
Designers should implement strategies to support ADA access to parking spots, bus stops, and Metro Mobility drop off points along protected bike lanes. Additional details will be forthcoming in a future update to the Street Design Guide. |
|
Intersection guidance |
See also bikeway intersection design guidance. |