2.10 Parkways
Search Content
Download PDF
Print Guide
Description
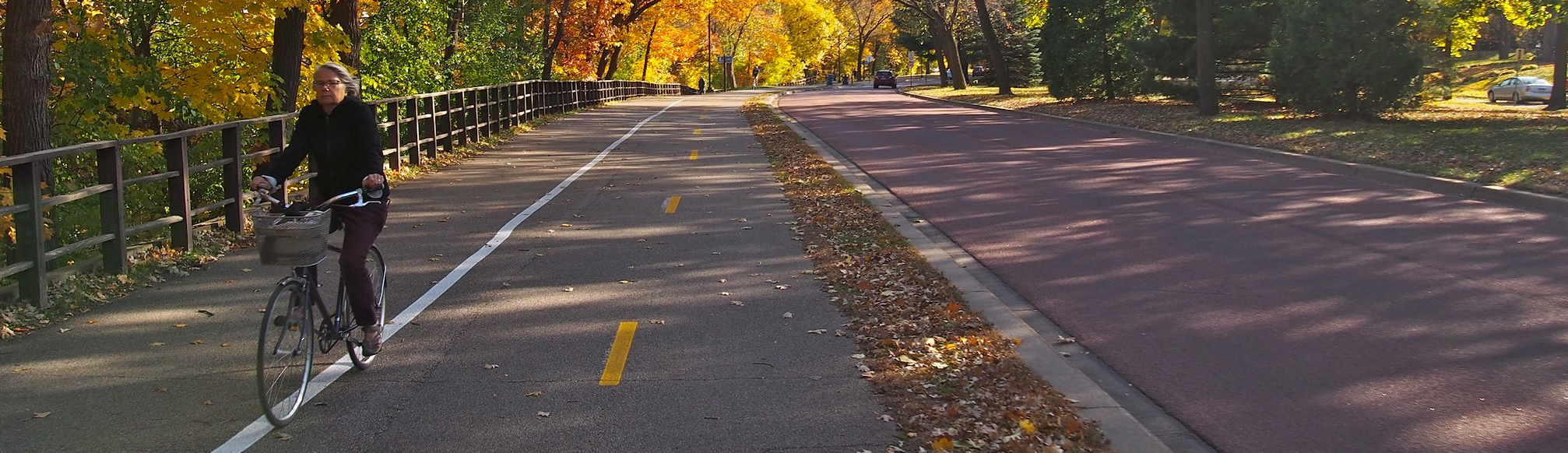
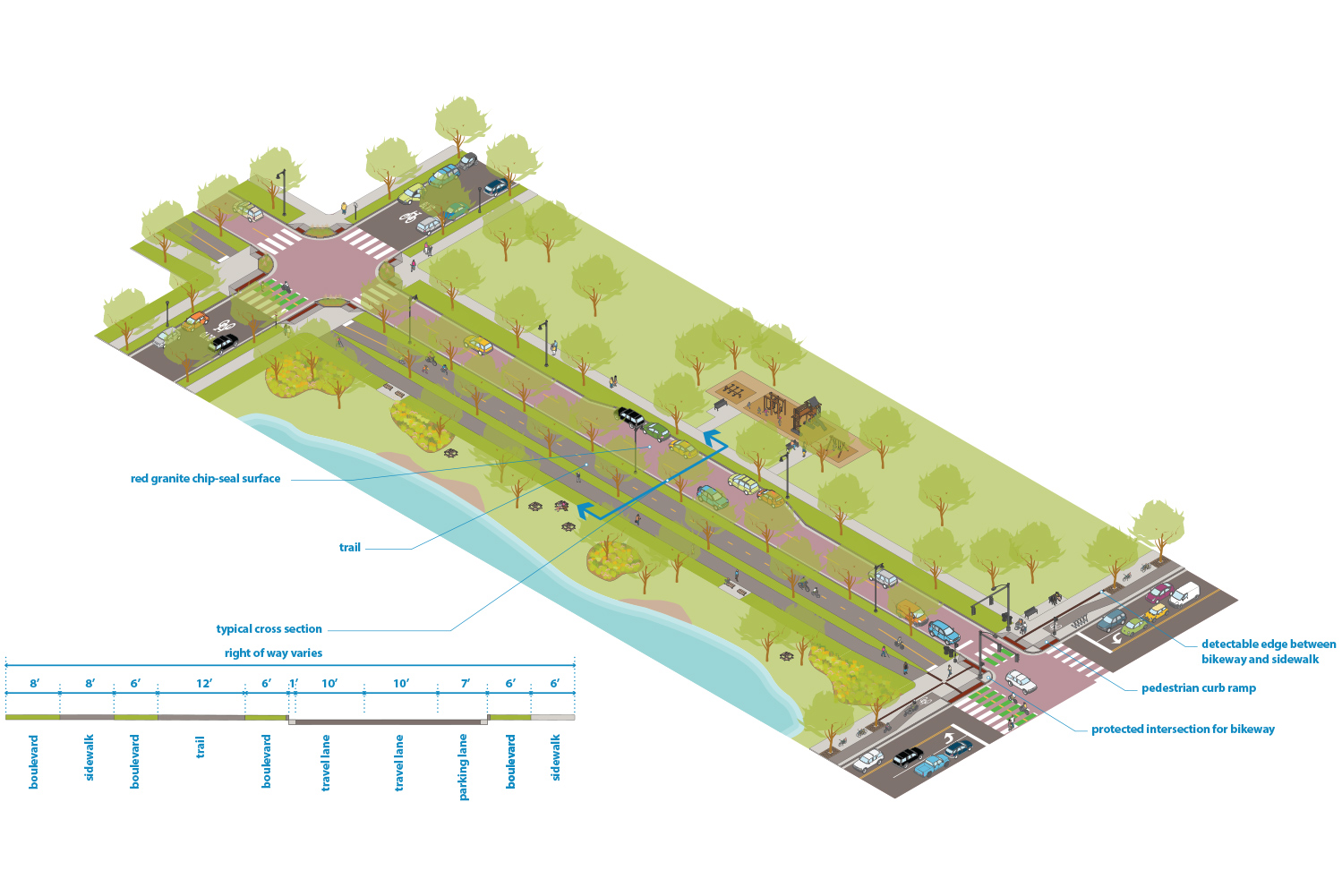
Parkways are under the jurisdiction of the Minneapolis Park and Recreation Board, typically are considered park land not public right of way, and support recreation and access to natural areas and community destinations across Minneapolis. Many parkways fall within the Grand Rounds parkway system, which is an interconnected system of parkways across the city and is eligible for the National Register of Historic Places. Parkways were originally planned and designed as linear parks and typically parallel rivers, streams, and lakes. While parkways can be attractive for non-recreational motor vehicle trips, these streets are not intended for through motor vehicle traffic.
Examples include Victory Memorial Parkway, West River Parkway, and Minnehaha Parkway.
Typical Characteristics
|
Miles |
53 miles |
|
Right of Way Width |
|
|
Effective Right of Way |
Varies |
|
Functional Class |
Local |
|
Jurisdiction |
Minneapolis Park and Recreation Board |
|
Route |
Local |
|
Modal Network |
All Ages and Abilities Bikeway Network |
|
Snow Emergency Route |
Not typically |
|
Historic Street |
No |
Typical Design and Operations
See Street Design Guidance chapter for more information
|
Sidewalk |
See sidewalks guidance for more details. |
|
Boulevard and Furnishing |
See boulevards and furnishings guidance for more details. |
|
Bikeway |
For parkways on the All Ages and Abilities bikeway network, see trail guidance for more details. 2-way bikeways or shared use paths should generally be used or 1-way bikeway if 2-way bikeway is not feasible. The trail and roadway can be immediately adjacent or separated by a significant amount of landscape, streams, or topography. |
|
Transit |
Except for a few locations, public transit is prohibited from parkways. |
|
Freight |
Not on the Truck Route Network. Trucks and commercial vehicles are prohibited from most parkways. |
|
Roadway |
|
|
Design speed |
25 or 20 mph See design speed guidance for more detail. |
|
Design vehicle |
Most commonly DL-23, but can also be SU-30 or WB-40 depending on intersecting street and context. See design and control vehicles guidance for more details. |
|
Control vehicle |
Generally Aerial Fire Truck Mid Mount 100. See design and control vehicles guidance for more details. |
|
Motor Vehicle Property Access |
Motor vehicle property access is limited along parkways. New driveways should be limited to locations without alley or cross street access. Driveway or access on and off parkways requires a permit from MPRB. See driveways guidance for more details. |
|
Intersection Traffic Control |
Stop control or signal control |
|
Intersection details |
|
Typical Cross Sections
Figure 2.10.1:
2-way Parkway street with trail