3.4E In-street curb-protected bike lanes
Search Content
Download PDF
Print Guide
Introduction
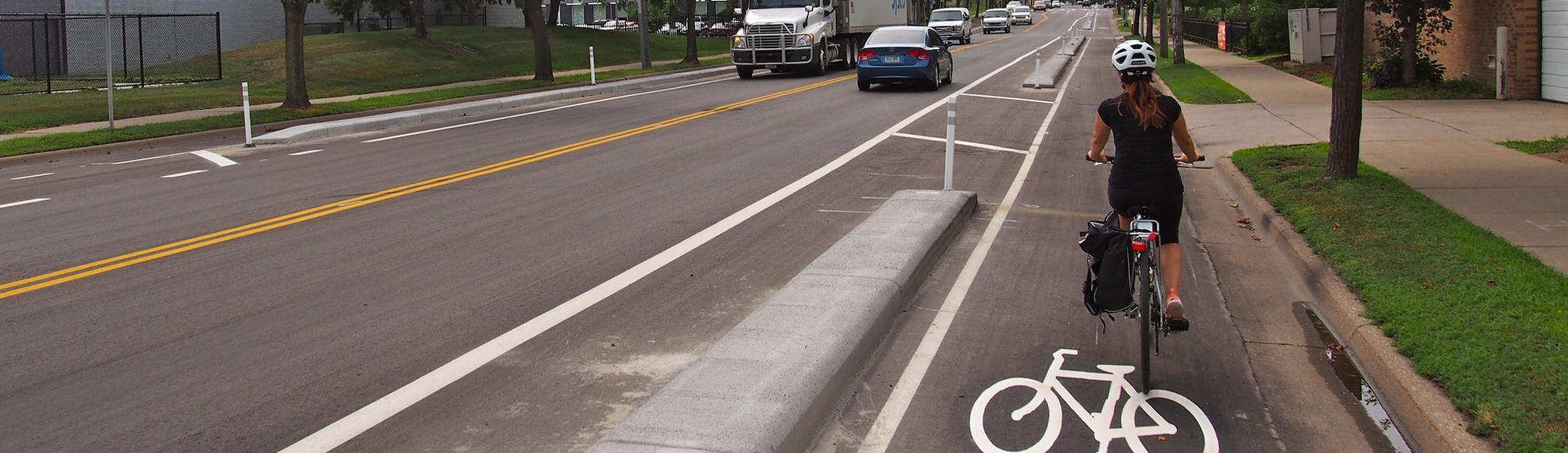
In-street concrete curb protected bike lanes utilize a form-in-place concrete curb installed on the roadway surface to provide physical separation from motorized traffic. Form-in-place concrete curbs provide numerous advantages over bollard-delineated bikeways, including reduced annual maintenance costs and reduced vehicular encroachment into the bike lanes. They are typically implemented as an upgrade to non-protected or delineator-protected bike lanes. The considerations in this section build on the guidance for delineator-protected bike lanes, which should serve as the starting point for any in-street curb-protected bikeway.

In-Street Curb-Protected Bike Lanes on Oak Grove St
Figure 3.4E.1:
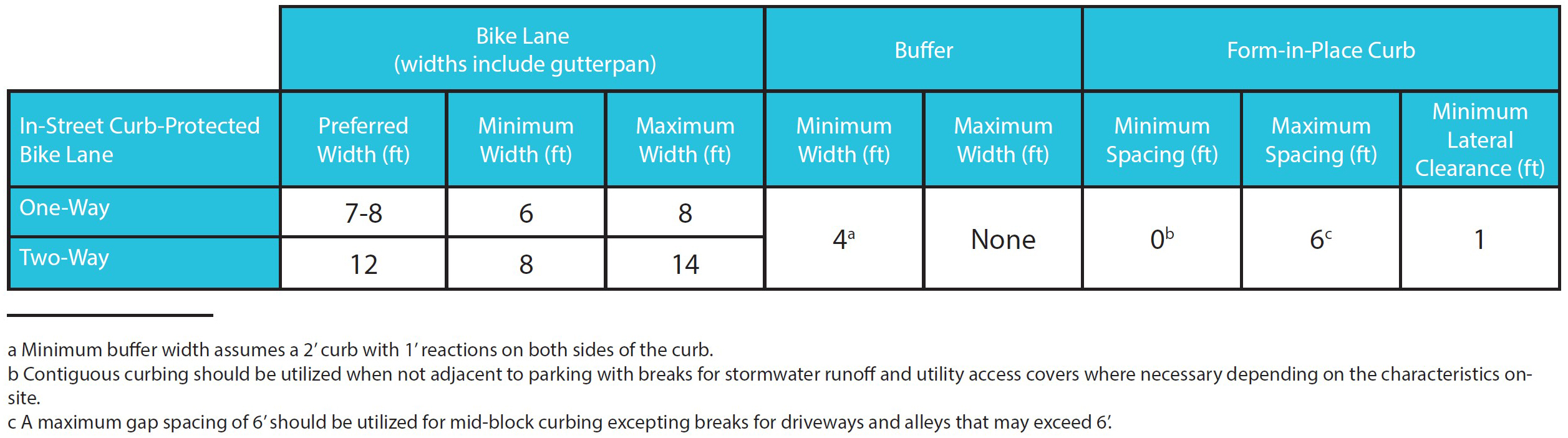
In-street curb-protected bike lane dimensions table
Figure 3.4E.2:
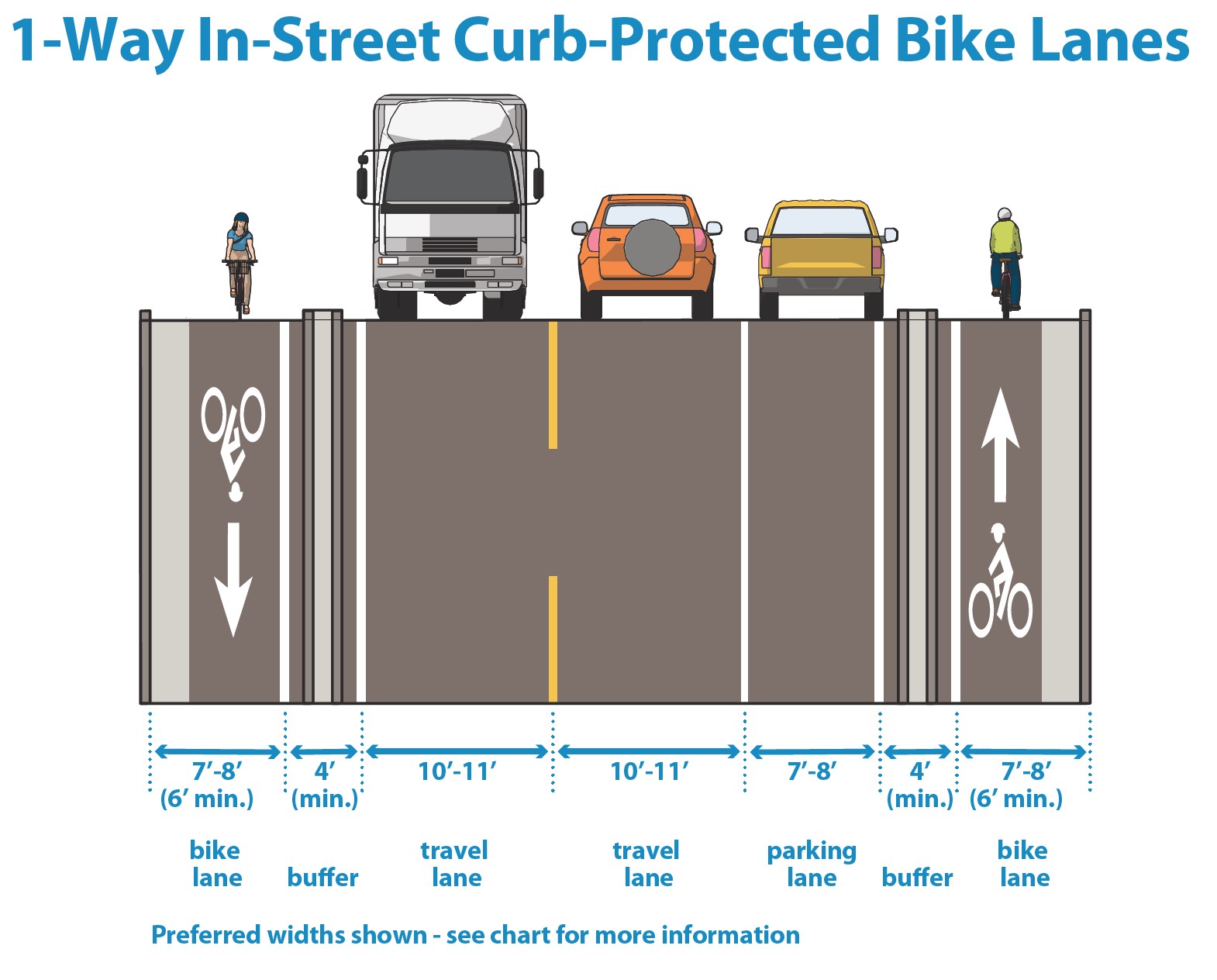
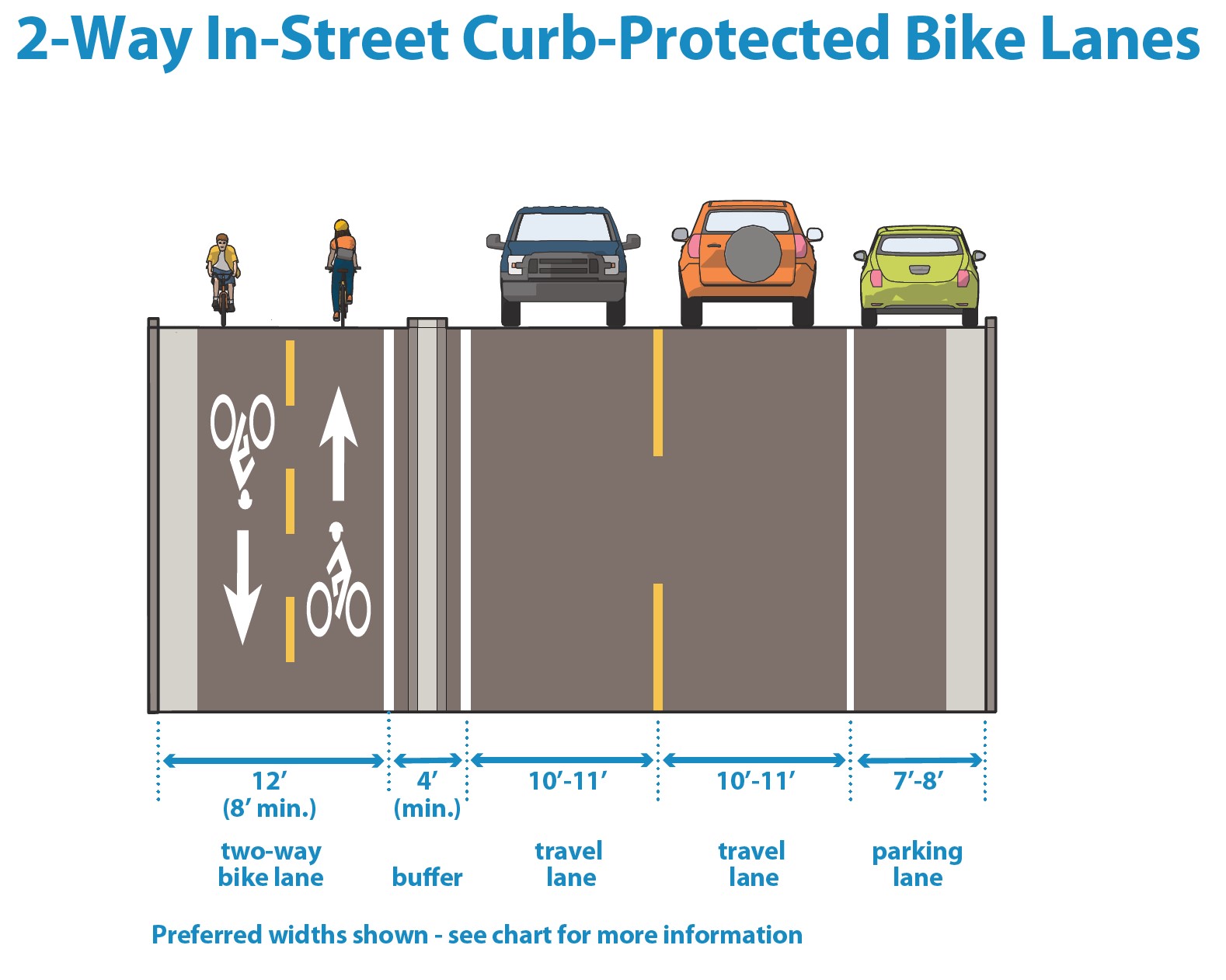
In-street curb-protected bike lane dimensions graphic
Design Considerations
Follow all appropriate guidance for delineator-protected bike lanes with additional design considerations below.
|
Maintenance |
Requires a minimum clearance of 6’ between curbs to accommodate snow clearance/removal. |
|
Bikeway curb width |
Typical form-in-place curb width is 2’. Narrower curb designs can be used when the bike lane is not adjacent to a parking lane, but curbs are not recommended to be narrower than 9”. |
|
Curb reaction |
A 1’ curb reaction should be assumed on either side of the form-in-place curb, for a total minimum bike lane buffer width of 4’ including the curb. |
|
Striping |
|
|
Bollard placement |
Plastic bollards should be placed at the beginning and end of each concrete curb section to inform winter maintenance operations. |
|
Bikeway curb breaks |
Should incorporate breaks for stormwater runoff and utility access covers where necessary depending on the characteristics on-site. |
|
On-street to off-street transitions |
May be designed to transition from on-street to sidewalk level in advance of intersections through the use of a slip ramp. |
|
Parking lane considerations |
|
|
Intersection guidance |
See also bikeway intersection design guidance. |